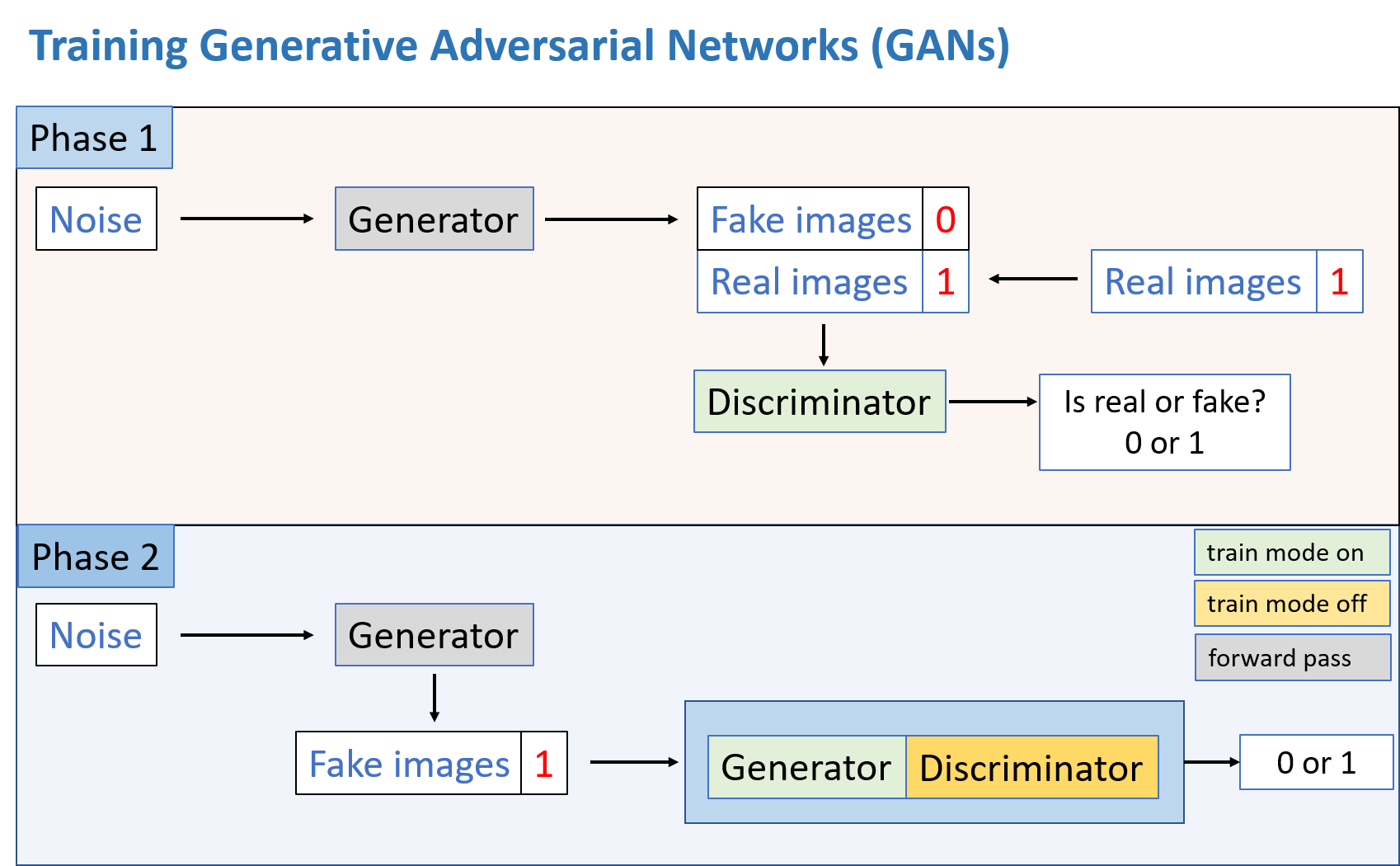
GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) are based on making two neural networks compete with each other. The first network, the generator, creates synthetic data from random noise (e.g. a sample normal distribution). The second network, the discriminator, tells whether the data given to it is real data or synthetic data.
Both these networks are trained alternately, one training step at a time. The figure above depicts the training process that happens in two phases. We will try to understand it in terms of image data.
Setup
- The coding size, i.e., the size of random noise is defined (e.g. 50).
- The network structure of the generator and the discriminator are defined.
- The first model contains only the discriminator.
- The second model is the GAN, which is obtained by concatenating the generator and discriminator, respectively.
Phase 1
- Random noise is given to the generator network. The forward pass through it produces the fake images.
- The fake images are combined with a batch of equal number of real images.
- The real images are given a labels ,
1, and the fake images are given the labels,0. - This batch of images and their labels are passed to the discriminator for one training step of the discriminator model.
- In this step the weights of the discriminator model are updated using true labels. The discriminator learns to identify real vs fake images.
Phase 2
- In this phase, the discriminator part of the GAN will have weights trained from previous step. The training mode of the discriminator is turned off in this phase. The generator part of the GAN has its training model on.
- A forward pass through the generator is performed to generate fake images.
- The labels of the fake images are set to
1. This is to make the GAN train on this data considering it to be real images. - The fake images and labels are passed to the GAN to train it for one training step. Note that in GAN at this step, only the generator part gets trained.
- The weights of generator part of the GAN are updated. The generator learns to make realistic images.
The two phases are repeated alternatively. The Phase 1 trains the discriminator to distinguish between real and fake images. The phase two trains the generator to create images are that realistic.
A simple implementation of GAN in Tensorflow is provided on this GitHub repository. It utilizes the mnist dataset.
The training considerations
Training GANs require good computational power. I was able to train the above linked GAN with only 10 thousand samples and it took about two hours to train for 50 epochs on google colab. Yet it was not able to generate good images.
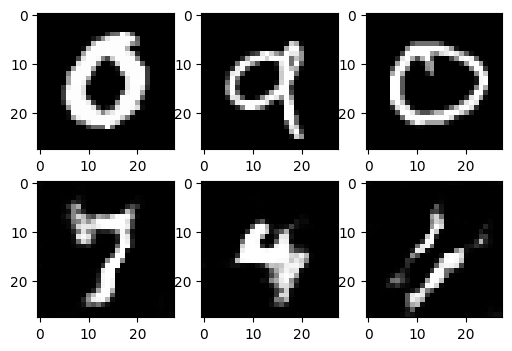
The first row in above figure shows the real images in mnist dataset and the second row show some of the images generated by the generator.
It is faster to train GANs on GPU, but this was just a demo for explaining the process.
Several adaptations of this method have been developed for various applications, one of which I use for my work. I will write about it sometime later.